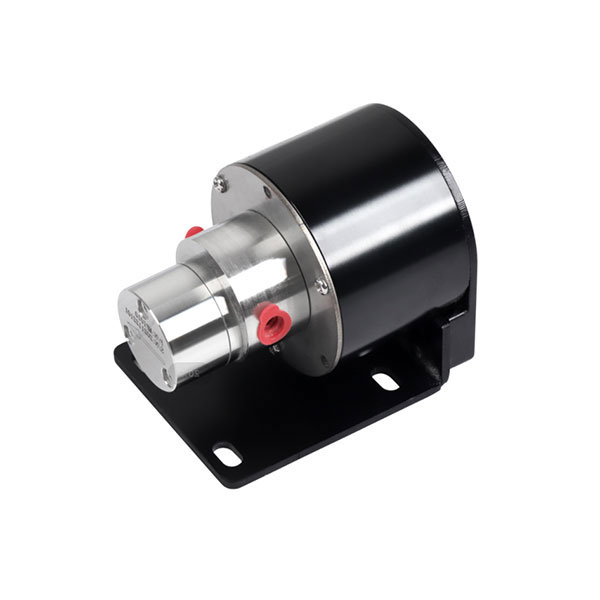
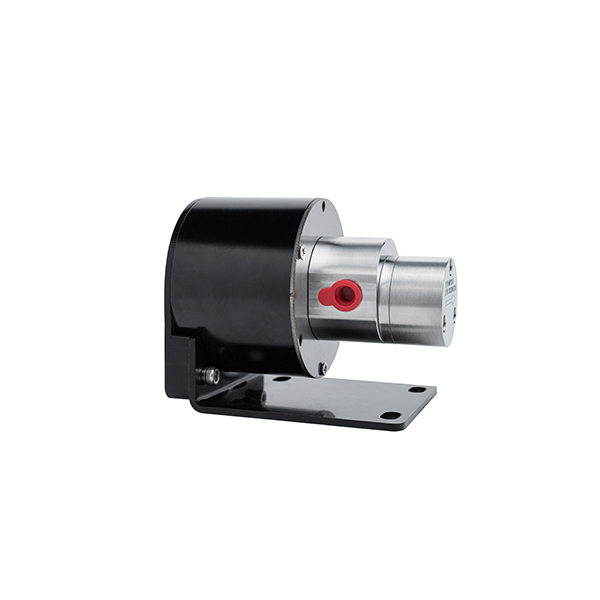
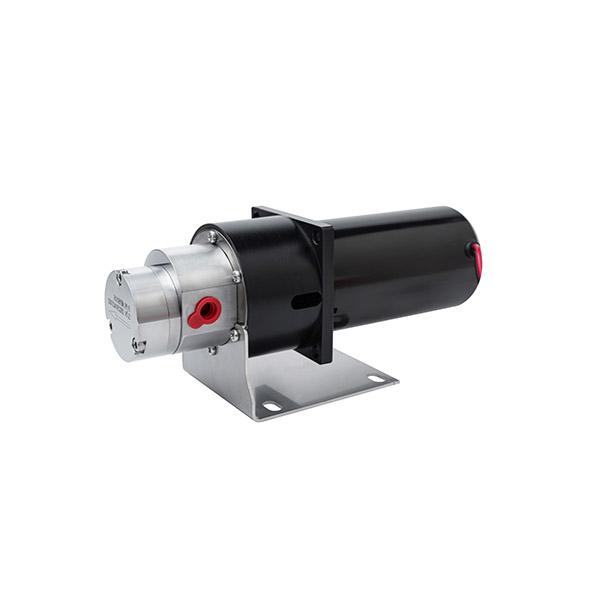
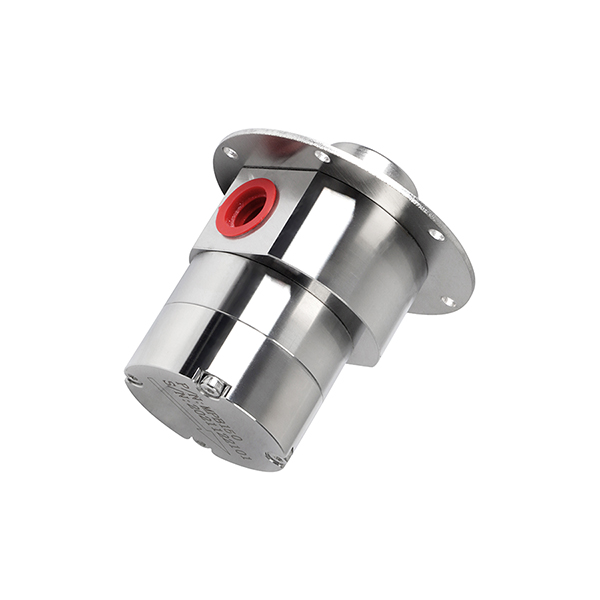
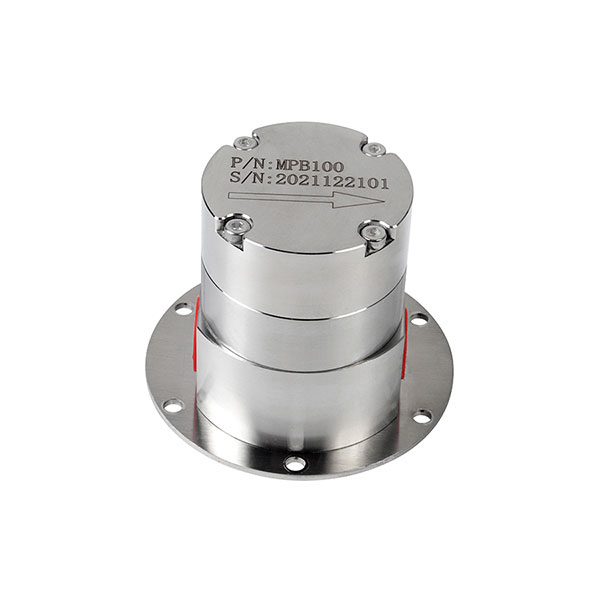
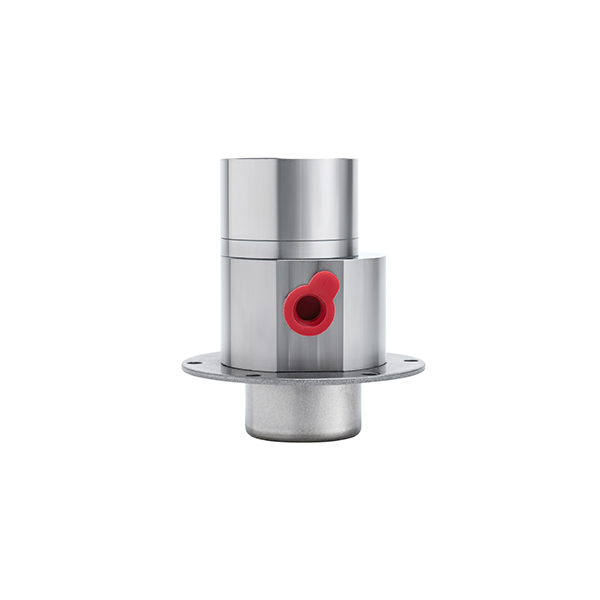
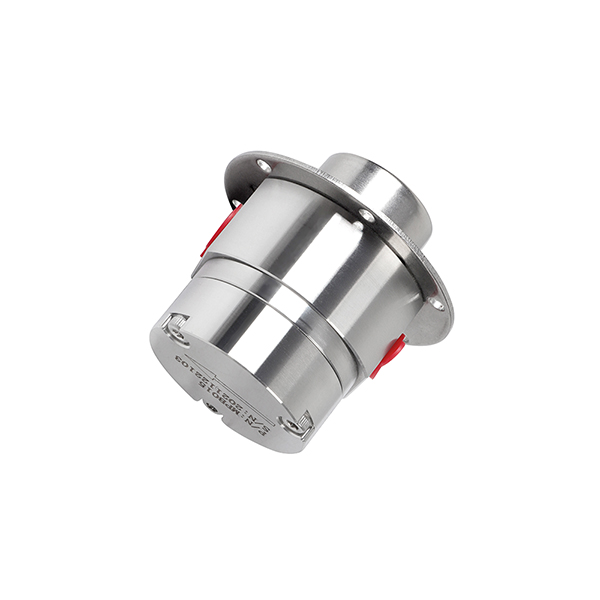
Applications of Micro DC Water Pumps
- Cooling systems – Maintaining consistent water flow for equipment temperature regulation.
- Laboratory experiments – Precise water delivery for controlled fluid handling.
- Water treatment systems – Dosing and chemical injection for water purification processes.
- Aquarium systems – Water circulation and filtration.
- Medical devices – Water-based fluid transfer in medical equipment.
- Hydraulic systems – Small-scale water-based hydraulic applications.
- Reverse osmosis systems – Water pumping for filtration and purification.
- Fuel cells – Providing controlled water flow for cooling and system hydration.
- Inkjet printing systems – Water flow management for printing technologies.
- Spray systems – Water delivery for spray applications in various industries.
Can Gear Pump Be Used for Water?
Yes, gear pumps can be used for water. These pumps are commonly used for transferring liquids, including water, because they provide steady, consistent flow. Gear pumps work by trapping water between two gears and forcing it through the pump. However, they are best suited for low-viscosity fluids
What Is the Difference Between AC and DC Water Pumps?
AC and DC water pumps are different in how they are powered and how they perform. AC (alternating current) pumps use electricity from a power grid, while DC (direct current) pumps use battery power or a DC power supply. AC pumps tend to be more powerful and are often used for larger applications, while DC pumps are more energy-efficient and better for small, portable systems. In general, AC pumps are good for continuous operation, while DC pumps are better for energy savings and portable use.